Definition of False-Fail Result
Usually there is a threshold of how close a match to a given sample must be achieved before the algorithm reports a match. The higher this threshold, the more false negatives and the fewer false positives. The false positive rate is the proportion of all negatives that still yield positive test outcomes, i.e., the conditional probability of a positive test result given an event that was not present. A false negative error, or false negative, is a test result which wrongly indicates that a condition does not hold. For example, when a pregnancy test indicates a woman is not pregnant, but she is, or when a person guilty of a crime is acquitted, these are false negatives. The condition «the woman is pregnant», or «the person is guilty» holds, but the test fails to realize this condition, and wrongly decides that the person is not pregnant or not guilty.
- He is a trained medical doctor and worked for Bain & Company as a consultant and as a CIO at SE-Consulting, among others, before founding the Scrum Academy.
- Although they display a high rate of false positives, the screening tests are considered valuable because they greatly increase the likelihood of detecting these disorders at a far earlier stage.
- When that occurs, additional test techniques can be used, such as analog open techniques to give incremental coverage on input or output pins.
- Farming households were failing to achieve their households’ basic food security from their small plots.
If the test system cannot detect this type of defect, then it is straightforward to understand why. Test result, which has reported an error, https://www.globalcloudteam.com/ but in fact there is no defect in the object of testing. In statistical hypothesis testing, this fraction is given the letter β.
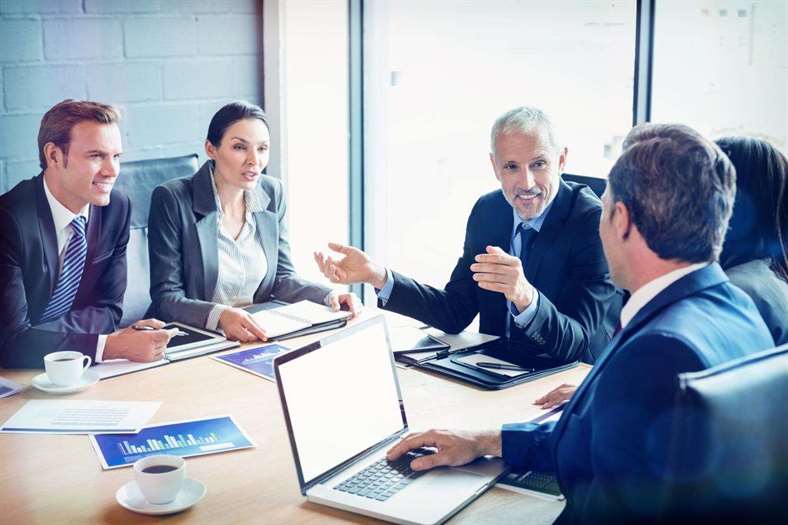
What is fail fast in Agile development?
Testing to compare two or more variants of a test item or a simulation model of the same test item by executing the same test cases on all variants and comparing the results. The degree to which a component or system is operational and accessible when required for use. The degree to which users can recognize whether a component or system is appropriate for their needs.
A system with a lower CER value provides more accuracy than a system with a higher CER value. Intuitively, type I errors can be thought of as errors of commission (i.e., the researcher unluckily concludes that something is the fact). For instance, consider a study where researchers compare a drug with a placebo. If the patients who are given what is false-fail result the drug get better than the patients given the placebo by chance, it may appear that the drug is effective, but in fact the conclusion is incorrect. In the example above, if the patients who got the drug did not get better at a higher rate than the ones who got the placebo, but this was a random fluke, that would be a type II error.
The quality of hypothesis test
In statistical hypothesis testing, this fraction is given the Greek letter α, and 1 −α is defined as the specificity of the test. Increasing the specificity of the test lowers the probability of type I errors, but may raise the probability of type II errors . A program of activities designed to improve the performance and maturity of the organization’s software processes and the results of such a program. The period of time that begins when a software product is conceived and ends when the software is no longer available for use.
The effect on the component or system by the measurement instrument when the component or system is being measured, e.g., by a performance testing tool or monitor. For example performance may be slightly worse when performance testing tools are being used. Modification of a software product after delivery to correct defects, to improve performance or other attributes, or to adapt the product to a modified environment. The ease with which a software product can be modified to correct defects, modified to meet new requirements, modified to make future maintenance easier, or adapted to a changed environment. Documentation defining a designated number of virtual users who process a defined set of transactions in a specified time period that a component or system being tested may experience in production. The capability of the software product to enable the user to learn its application.
Can you solve 4 words at once?
The capability of the software product to provide the right or agreed results or effects with the needed degree of precision. A collaborative approach to development in which the team and customers are using the customers own domain language to understand their requirements, which forms the basis for testing a component or system. Product Owner Product Owner Journey Become a product owner and learn how to implement agile product development. A 360 review (360-degree review) is a continuous performance management strategy aimed at helping employees at all levels obtain … Subscription management is the process of overseeing and controlling all aspects of products and services sold repeatedly through…

The degree to which a component or system allows only authorized access and modification to a component, a system or data. Supplied software on any suitable media which leads the installer through the installation procedure. Supplied instructions on any suitable media, which guides the installer through the installation process.
Processor Boot Solution Addresses High-Rel Edge Space Systems
Reports are prepared that compare the actuals to that which was planned. The process of developing and prioritizing test procedures, creating test data and, optionally, preparing test harnesses and writing automated test scripts. A customized software interface that enables automated testing of a test object. The process of running a test on the component or system under test, producing actual result.

Is that false is untrue, not factual, factually incorrect while fail is that is a failure. If tests cannot be added at this stage, then other test stages can be informed of the deficiency and tests can be developed if required. The escaped defects, identified this way, can be used as a relevant starting point for any diagnostic when tests fail at later stages. The same is true for a simulated high and the open pin floating high case. In some cases, it may be difficult to generate vectors that can test all inputs.
failing
A graphical model representing the relationship of the amount of testing per level, with more at the bottom than at the top. A five-level staged framework for test process improvement, related to the Capability Maturity Model Integration , that describes the key elements of an effective test process. The planning, estimating, monitoring and control of test activities, typically carried out by a test manager.

A skilled professional who is involved in the testing of a component or system. A way of developing software where the test cases are developed, and often automated, before the software is developed to run those test cases. The execution of a test suite on a specific version of the test object. A formula based test estimation method based on function point analysis. The purpose of testing for an organization, often documented as part of the test policy.
From Design to Delivery: Creating Embedded System Solutions
It is standard practice for statisticians to conduct tests in order to determine whether or not a «speculative hypothesis» concerning the observed phenomena of the world can be supported. The results of such testing determine whether a particular set of results agrees reasonably with the speculated hypothesis. We reject H0 [i.e., the hypothesis to be tested] when it is true, we fail to reject H0 when some alternative hypothesis HA or H1 is true.